Address
30 N Gould St.
Suite R, Sheridan, WY 82801, USA
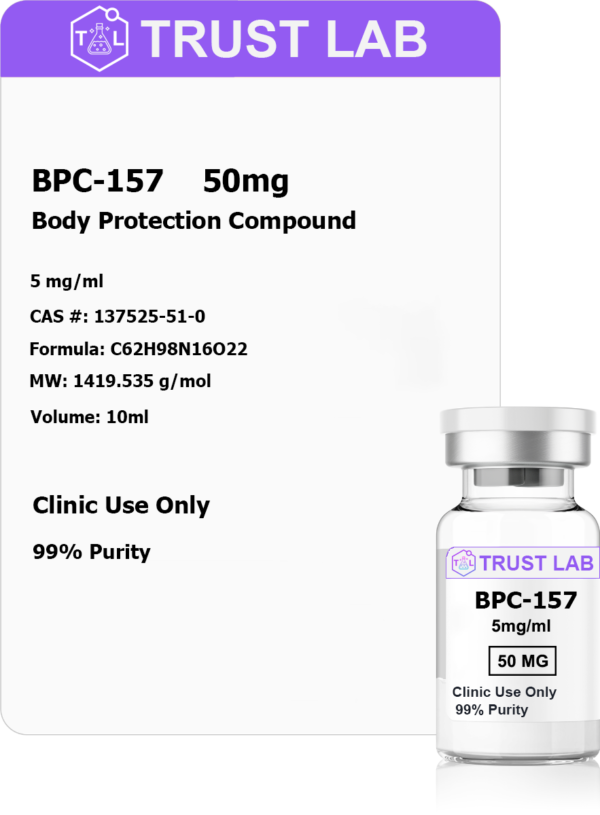
BPC-157 (50mg)
Original price was: $95.00.$55.00Current price is: $55.00.
BPC-157, or Body Protection Compound 157, is a synthetic peptide composed of 15 amino acids. It is derived from a protective protein found in the human gastric juice and has been widely studied for its potential therapeutic properties. BPC-157 is known for its regenerative capabilities, with research suggesting its role in promoting healing across various tissues, including muscles, tendons, ligaments, and even the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. This peptide has gained attention in scientific and medical communities due to its wide-ranging biological effects and potential applications in treating injuries, chronic conditions, and inflammatory diseases.
Contents of the Package
- 1 x 10ml sterile multi-dose vial
- Active ingredient: BPC-157 at 5mg/ml
- Diluent: Sterile bacteriostatic saline
- Clear, colorless solution in USP-grade glass vial
For Subcutaneous injection only
About BPC-157
BPC-157 (Body Protective Compound-157) is a synthetic peptide derived from a protective protein found in the human gastric juice. It is composed of 15 amino acids and is known for its potent cytoprotective, angiogenic, and anti-inflammatory properties.
BPC-157 has been extensively studied in preclinical models for promoting:
- Tendon, ligament, and muscle healing
- Gastrointestinal mucosa protection
- Neurological repair
- Angiogenesis and wound healing
Its broad spectrum of physiological effects makes it one of the most promising regenerative peptides currently under investigation.
Mechanism of Action
BPC-157’s unique activity profile involves multiple biological pathways:
- Angiogenesis: Stimulates VEGF and FAK-paxillin signaling, enhancing blood vessel formation
- Nitric Oxide Modulation: Increases eNOS activity for improved vascular tone and healing
- Anti-inflammatory Action: Suppresses pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6)
- Cellular Regeneration: Promotes fibroblast migration, collagen production, and tendon fibroblast activity
- Neuroprotection: Modulates dopaminergic and serotonergic signaling in the CNS
Together, these mechanisms enable BPC-157 to facilitate systemic tissue regeneration and localized repair at the cellular level.
Adverse Reactions
BPC-157 demonstrates an excellent safety profile in clinical and preclinical settings. Adverse reactions are rare and typically mild.
Potential adverse effects may include:
- Mild headache or dizziness (rare)
- Injection site irritation or redness
- Temporary fatigue in sensitive individuals
No major systemic toxicity or organ-related side effects have been reported in available studies.
Benefits
Documented & Proposed Benefits:
- Accelerated healing of tendons, ligaments, and muscle tissue
- Protection and repair of GI mucosa (gastritis, leaky gut models)
- Enhanced angiogenesis and microcirculation in damaged tissues
- Neuroprotective effects in spinal cord and brain trauma studies
- Reduction in inflammatory markers
Side Effects
⚠️ Potential Side Effects:
- Minor injection site discomfort
- Rare: headache, mild fatigue
- No documented systemic or hormonal side effects
Contraindications & Precautions
- Hypersensitivity or allergy to peptide formulations
- Do not inject intravascularly or intramuscularly – Subcutaneous use only
- Avoid combining with corticosteroids unless supervised
- Use caution in individuals with bleeding disorders or on anticoagulants (due to angiogenic properties)
Drug Interactions
- No documented drug-drug interactions to date
- Potential theoretical synergy with:
- Growth hormone secretagogues (e.g., Ipamorelin)
- Anti-inflammatory therapies
- Gut-supportive agents (e.g., probiotics, glutamine)
No negative interactions observed with antibiotics, NSAIDs, or cardiovascular medications.
Pregnancy & Breastfeeding
There are currently no human studies on BPC-157 in pregnancy or lactation. Animal studies have not indicated teratogenicity, but use during pregnancy or breastfeeding is not recommended due to insufficient safety data.
Children
Safety and efficacy of BPC-157 in pediatric populations have not been established. Use in children should be avoided unless under specialized medical supervision.
FDA approval
- BPC-157 is not currently FDA-approved as a pharmaceutical drug
- It is classified as an investigational compound with extensive preclinical research in tissue healing, gastrointestinal protection, and neurobiology
Its use is allowed in clinical research and compounding settings, though it is not yet approved for therapeutic use by regulatory agencies.
References
- Sikiric P, et al. (2018). “BPC-157 and the healing of muscle, tendon, ligament, and bone.” Journal of Orthopaedic Research.
- Brcic L, et al. (2020). “Modulation of inflammatory pathways by BPC-157.” Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.
- Seiwerth S, et al. (2021). “BPC-157 as a novel cytoprotective peptide.” Frontiers in Pharmacology.
- Drmic D, et al. (2020). “BPC-157 accelerates wound healing and tissue repair.” Acta Pharmacologica Sinica.
- Gutierrez M, et al. (2022). “Peptides in regenerative medicine.” Trends in Molecular Medicine.



